Climate Change : Initiatives
Renewable Energy
For renewable energy businesses, MC has set a goal to double its renewable power generation capacity by FY2030 compared to FY2019. In line with the global shift toward renewable energy as a primary power source, MC is expanding its investments and initiatives across the value chain. This includes areas from power generation to energy retail, with a focus on renewable energy. A key example of this strategy is MC’s 2020 acquisition of Eneco, a Dutch integrated energy company that operates throughout Europe. By combining digital technologies with environmentally-friendly energy sources, including renewable energy, MC aims to ensure a stable supply of power and deliver new forms of value to customers. These benefits include enhanced supply and demand adjustment functions. In addition, MC is pursuing initiatives in hydrogen, which is expected to play an important role as a next-generation fuel. Through these efforts, MC seeks to contribute to global decarbonization while also strengthening its corporate value.

Initiatives in Europe for the Promotion of Renewable Energy
Eneco is an integrated energy company operating mainly in the Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany. Its businesses include power generation, power and gas trading, power and gas retail services, and district heating, with an emphasis on renewable energy. Eneco holds the third largest customer base in the Netherlands and owns approximately 2.8GW of renewable energy assets as of the end of March 2025. Since 2007, Eneco has led the development of renewable energy ahead of many competitors. It has established itself as a green brand by supplying consumers with 100 percent green energy since 2011, including through the use of green certificates. Eneco has also been recognized as an innovator that prioritizes customer-focused services. In addition, in 2021, Eneco announced its One Planet Plan, which aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2035. This plan covers CO2 emissions from the company’s own operations, referred to as Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, as well as emissions across its entire value chain, known as Scope 3 emissions. These include emissions from electricity and gas retailing and from supplying heat to businesses and households. Eneco is widely recognized in both domestic and international contexts as a company that is proactively addressing climate change.
MC aims to help establish a sustainable society by achieving economic, societal, and environmental growth simultaneously. By leveraging Eneco's technology and expertise, MC is accelerating the development of renewable energy both within Europe and beyond. MC also intends to enhance energy management services for Eneco customers by combining Eneco’s strong customer base with MC’s broad range of products and services.
The power industry is undergoing a significant transition driven by the expansion of decentralized power sources, advances in battery storage, and the rapid development of digital technologies. These changes have emerged alongside the increased adoption of renewable energy. In this evolving environment, MC and its partner Chubu Electric Power aim to address societal issues such as the transition to a decarbonized society and the preservation of the global environment. Both companies seek to support essential infrastructure and foster the growth of Eneco, which provides customer-centered energy services based on renewable energy and digital technologies.

EV/Batteries
The transportation sector currently accounts for approximately 20% of global CO2 emissions. Reducing both CO2 emissions and the reliance of fossil fuels in the automobile industry has therefore become a critical challenge. As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular due to their low environmental impact while in operation, MC aims to contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society through business activities centered on EVs and batteries.
Activities with Honda
ALTNA Co., Ltd. was established in July 2024 as a joint venture with Honda Motor Co., Ltd. (Honda) to develop new businesses that address the anticipated expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) market and support a decarbonized future. By combining Honda's advanced EV and battery control and connectivity technologies with MC’s expertise in energy businesses—including battery energy storage and smart-charging operations—ALTNA is creating business models that reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for EV users and promote the long-term utilization of EV batteries. Details on these businesses are outlined below.
1. Battery Leasing Business
ALTNA collaborates with vehicle owners and leasing companies by retaining ownership of EV batteries and leasing them for the duration of the vehicle lease. Through continuous monitoring of battery usage, ALTNA supports long-term use, including for second-hand leased vehicles. After their automotive life, recovered batteries are repurposed for stationary storage applications. By setting lease prices based on long-term battery value and reuse, ALTNA works to reduce overall EV usage costs.

2. Battery Repurposing Business
ALTNA supplies power using repurposed in-vehicle batteries as system storage batteries. In response to growing demand for battery capacity to support renewable energy deployment, ALTNA operates a resource-recycling grid storage plant that maximizes storage utilization by assuming battery replacement over time. Additionally, ALTNA ensures appropriate recycling of end-of-life grid storage batteries, supporting resource-circulation-oriented manufacturing.

3. Smart Charging Business
Utilizing advanced energy control technologies, ALTNA provides smart charging services that optimize electricity costs for EV users. By simply plugging in their vehicle, users can automatically charge during off-peak hours, reducing energy costs. ALTNA’s charging plans also support increased use of renewable energy by scheduling charging during periods of surplus renewable generation on the grid.

Low-carbon Hydrogen & Ammonia/SAF
Low-carbon Hydrogen & Ammonia
MC is focusing on low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia, which are viewed as promising next-generation energies. We are advancing studies with our partners across each stage of the low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia supply chain: production, transportation, and storage.
At the production stage, MC is exploring participation in ExxonMobil’s planned low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia project in Baytown, Texas, USA, as well as the potential offtake of low-carbon ammonia in partnership with Idemitsu Kosan.
This project aims to begin producing approximately 900,000 tons of low-carbon hydrogen per year and over 1 million tons of low-carbon ammonia per year by 2029, and is expected to become the world's largest project of its kind. This project intends to produce hydrogen that is virtually carbon-free by removing roughly 98% of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, enabling the production of low-carbon ammonia as well.
At the transportation and storage stages, MC is evaluating the partial conversion of its Namikata LPG Terminal into an ammonia terminal, enabling the supply of low-carbon ammonia for various industrial uses, especially in the Shikoku and Chugoku regions. To support efficient ammonia carrier operations, MC is also studying coordination with the ammonia terminal that Idemitsu Kosan plans to establish in the Shunan region of Yamaguchi Prefecture.
Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen is gaining attention as a low-carbon energy source. MC participated in the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)-subsidized Demonstration of Unused Energy-Based Hydrogen Supply Chain Using Organic Chemical Hydride Method* project, which was successfully concluded in December 2020 and has now progressed to commercial project development. MC is actively working to build an international hydrogen value chain connecting clean-hydrogen-producing countries with consuming regions.
- *This demonstration project aimed to establish the mass transport and supply technologies needed for full-scale hydrogen power generation by 2030, in line with Phase Two of METI's Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells (initially published in June 2014 and revised in March 2016). In 2020, MC conducted a demonstration transporting hydrogen from Brunei to Japan. In line with the Paris Agreement adopted at COP21 in December 2015 and the growing need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, MC aims to contribute to the large-scale use of hydrogen—which emits no CO2 during combustion—for power generation.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
Among the various initiatives aimed at achieving a low-carbon and decarbonized society, we are promoting the commercialization of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) as a practical solution for decarbonizing the aviation sector, where hydrogenation and electrification remain technically challenging.
Par Pacific, Mitsubishi, and ENEOS to Establish Joint Venture for Renewable Fuels in Hawaii
In July 2025, Par Pacific Holdings, Inc., MC, and ENEOS announced the signing of definitive agreements to establish Hawaii Renewables, LLC, a joint venture to produce renewable fuels at Par Pacific’s refinery in Kapolei, Hawaii. MC and ENEOS will acquire a 36.5% equity stake in Hawaii Renewables in exchange for $100 million in cash consideration.This strategic partnership brings together Par Pacific’s advantaged U.S. West Coast and Pacific asset base and operational capabilities with MC’s global integrated business and feedstock procurement expertise, as well as ENEOS’s fuel refining and trading capabilities across the Asia-Pacific and North America.
Front-End Engineering Design for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Production at Wakayama Refinery
In collaboration with ENEOS Corporation, we are currently conducting Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) to advance the study of a SAF production facility at the ENEOS Wakayama Plant in Japan. Subject to the result of the FEED, the facility is expected to produce approximately 300,000 tons (400,000 KL) of SAF per year from FY2028 onward, along with bio-naphtha and bio-diesel fuel fractions as byproducts. Feedstock is expected to include used cooking oil, animal fat, and other waste-derived materials. ENEOS provides an established sales network, manufacturing and refining technologies, and expertise in feedstock procurement, while MC brings procurement capabilities both in Japan and globally. By combining their respective strengths, ENEOS and MC will accelerate the study with the goal of developing large-scale SAF production in Japan.
CCUS
MC recognizes that Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), as well as Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), will play a major role in achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement. The International Energy Agency (IEA) states that CCUS must be deployed to reduce roughly 1.5 billion tons of CO2 emitted in 2050 to meet the 1.5°C target. Because CCUS spans multiple industries—from CO2 emitting sectors to those producing end products such as fuels, chemicals, and construction materials—MC views CCUS as a business opportunity well suited to its broad industrial capabilities. To capture this opportunity, MC is actively promoting the commercialization of CCUS.
For Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU), MC is pursuing short-term initiatives in the construction materials sector, where commercialized products and technologies already exist (e.g., concrete). MC is also advancing medium- to long-term initiatives in the petroleum and chemicals sector, where further research and development and demonstration are still required (e.g., jet fuel and synthetic fibers). Through these efforts, MC is developing new businesses and technologies through investments and collaborations with Japanese and international partners. MC is also accelerating efforts to build overseas CCS value chains.
Additionally, the IPCC* states that achieving the 1.5°C target requires not only reducing CO2 emissions at the source, but also implementing Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) technologies to remove remaining CO2 from the atmosphere. MC sees this as another business opportunity and is pursuing technologies such as Direct Air Capture (DAC), a leading CDR method that captures CO2 directly from the atmosphere.
- *Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The IPCC is an intergovernmental body established by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) to collect and assess scientific research related to climate change.
Initiatives in the Field of Construction Materials
MC is active in the construction materials field, where technologies are already mature and commercial projects are in operation. Construction materials range from ready-mixed concrete and precast concrete (block products) to aggregates (raw material of concrete). Because each product requires different CO2-reduction approaches, MC aims to maximize emissions reductions by applying a combination of technologies and corporate partnerships—its Green Concrete Concept.
CarbonCure
CarbonCure Technologies Inc. is a Canadian company with technology that mineralizes CO2 into concrete materials. MC has taken an equity stake in CarbonCure and formed a business partnership to expand deployment of CarbonCure's technology. CarbonCure's carbon-recycling system injects purified CO2 into fresh concrete during production, reducing CO2 emissions by enabling lower cement usage.
The resulting concrete maintains the same strength and reliability as conventional concrete and is already in wide commercial use, particularly in North America.
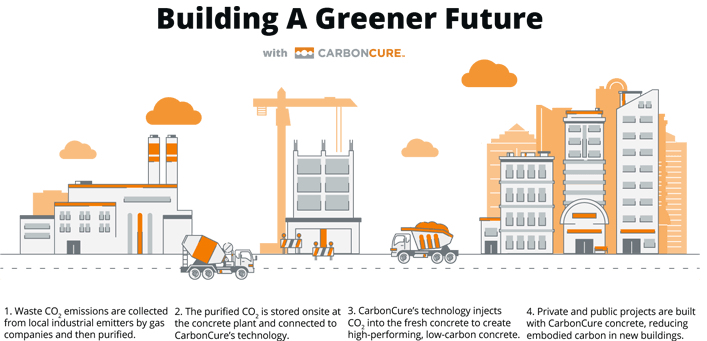
- Emitted CO2 is collected and refined.
- The refined CO2 is delivered and stored at concrete plants equipped with CarbonCure's systems.
- CO2 is injected into fresh concrete, producing low-carbon concrete.
- By using concrete incorporating CarbonCure technology, overall CO2 emissions from building materials are reduced.
Initiatives in the Petroleum and Chemicals Field
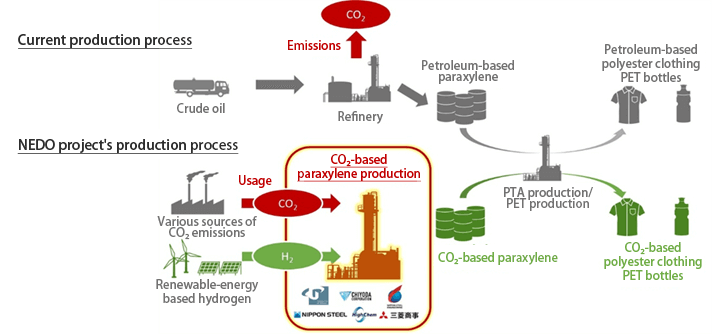
As part of its medium- to long-term CCUS strategy, MC is working in the petroleum and chemicals sector, where additional research and development is required. Together with the University of Toyama, Chiyoda Corporation, Nippon Steel Engineering Co., Ltd., Nippon Steel Corporation, and HighChem Company Limited, MC was selected for a NEDO-commissioned project titled: “Carbon Recycling and Development of Next-Generation Thermal Power Generation/Development of Technology for the Reduction of CO2 Emissions and the Effective and Practical Use of CO2/Development of Technology for the Use of CO2 in Chemical Materials.” The partners are developing a method to produce paraxylene, a key material used in clothing fibers and PET bottles, from CO2. Leveraging its position as one of the world’s largest paraxylene traders, MC is responsible for testing and evaluating the commercial feasibility of CO2‑derived paraxylene using its global network. Due to its chemical structure, paraxylene can incorporate CO2 while requiring relatively little hydrogen as a feedstock. MC sees significant potential for CCU-based paraxylene from both economic and environmental perspectives. As global populations grow, demand for clothing is expected to rise, creating additional demand for polyester beyond what can be met through recycling alone. MC aims to replace petroleum-derived paraxylene with sustainable paraxylene produced from CO2.
CCUS at Tangguh LNG Project
MC, together with operator bp, reached Final Investment Decision (FID) at the end of 2024 on the development plan for the Tangguh LNG Project in West Papua, Indonesia, including a large-scale CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage) initiative. The plan aims to capture approximately 15 million tons of CO₂ and reinject it into the Vorwata gas field for permanent storage. This will not only reduce CO₂ emissions but also enhance production efficiency and increase natural gas output. Project development began in 2025, with CCUS operations expected to start in 2028.
-
Project location map -

LNG facility
Initiatives Toward Establishing Overseas CSS Value Chains
MC is conducting a feasibility study on building an overseas CCS value chain through the Oceania CCS Project and the Northern Offshore of Peninsular Malaysia CCS Project, both selected as Advanced CCS Projects for FY2025 by the Japan Energy and Metals National Corporation (JOGMEC).
In the Oceania CCS Project, Mitsubishi Corporation, Nippon Steel Corporation, ExxonMobil Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd., Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, and Mitsubishi Corporation Clean Energy Ltd. are studying CO2 capture from Ise Bay/Chubu area and the transport and storage of this CO2 in the Asia-Pacific region, including Australia, Malaysia, and Indonesia. In the Northern Offshore of Peninsular Malaysia CCS Project, Mitsubishi Corporation, ENEOS Corporation, ENEOS Xplora Inc., JFE Steel Corporation, Cosmo Oil Co., Ltd., Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd., and PETRONAS CCS Solutions Sdn Bhd are studying CO2 capture from the Tokyo Bay area and its transport and storage at sites offshore northern Peninsular Malaysia. Both projects include studies on CO2 separation, capture, transport, and storage, with the goal of commencing storage operations by FY2030.
Carbon Credit
Collaboration with South Pole on the Carbon Credit Trading Business Based on CCUS and Other Innovative Carbon Removal Technologies
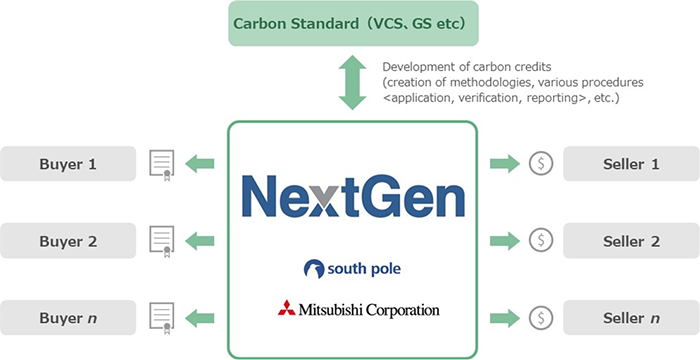
MC and the Swiss company South Pole, one of the world’s largest carbon credit developers, have jointly established NextGen CDR AG (NextGen) as a venture to manage the procurement and sales of carbon credits derived from Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) and other innovative carbon removal technologies.
To achieve the goals outlined in the Paris Agreement and keep global warming below 1.5°C, the adoption of carbon removal technologies such as CCUS is essential. However, several challenges must be overcome before these technologies can be deployed at scale, including the need for further technological innovation and cost reduction. MC is working to address these issues by creating new revenue streams for credit suppliers through credit sales. To this end, we are bringing together carbon credit buyers and establishing long-term offtake agreements, with the aim of accelerating the widespread implementation of these early-stage technologies.
Overview of Project (NextGen CDR AG)
Overview of Project (NextGen CDR AG)
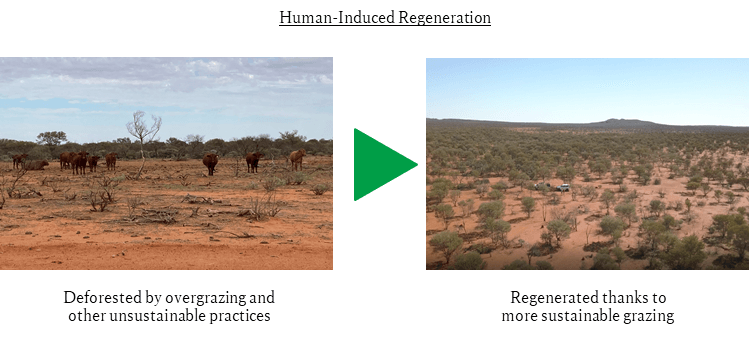
Regeneration Project/Investment in Australian Integrated Carbon
MC and Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha (NYK) have jointly acquired a 40% interest in Australian Integrated Carbon Pty Ltd (AIC), a company engaged in the sale of carbon credits. These credits are generated through CO2 sequestration achieved via the regrowth of Australia’s native forests using a process known as human-induced regeneration, an established methodology in Australia. This approach introduces new land-management practices to support the regeneration of native woodlands that have been lost over the past few centuries due to clearing and overgrazing. The amount of CO2 stored in the regenerated forests is officially certified as Australian Carbon Credit Units by the Australian government. Through its expanding portfolio, AIC aims to contribute to capturing up to 5 million tons of CO2 emissions per year, with a cumulative total of 85 million tons by 2050.
Other Low-Carbon/Decarbonized Businesses (Green Logistics, Green Buildings, etc.)
We will leverage our extensive networks across various industries to promote carbon reductions and decarbonization in multiple fields, beginning with green logistics and green buildings.
Participation in the Breakthrough Energy Catalyst Program to Accelerate the Application of Decarbonization Technologies in Society
MC is the first company in Asia to participate in Breakthrough Energy Catalyst (BEC), a program dedicated to accelerating the deployment of innovative decarbonization technologies.
BEC is a new initiative under Breakthrough Energy, the network of programs founded in 2015 by global philanthropist Bill Gates. The BEC program provides investment and other forms of support for individual projects based on next-generation decarbonization technologies that have completed their research and development phase.
MC has been active in the renewable energy sector and has begun exploring the introduction of next-generation energy sources such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanation. We recognize the importance of harnessing new technologies and innovations to meet the global challenge of transitioning to a carbon-neutral society.
In addition, BEC acts as a “catalyst”, connecting funding from private-sector partners and philanthropic organizations, product offtake support for consumers of green products, and assistance from government agencies. Through these efforts, BEC is creating a framework to scale projects based on innovative decarbonization technologies that are nearing commercialization, contributing to the realization of a carbon-neutral society.
BEC currently focuses on five priority areas: (1) clean hydrogen production (and related infrastructure), (2) long-duration energy storage (LDES), (3) sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), (4) direct air capture (DAC), and (5) green manufacturing industries (steel, cement, plastics, etc.). In the future, BEC may broaden its scope to include additional technologies important for decarbonization. MC considers these technologies essential to its EX Strategy and its Roadmap to a Carbon-Neutral Society.
Our participation in BEC will enable us to support the adoption of innovative technologies that accelerate the transition to a carbon-neutral world and help reduce environmental impact without compromising people’s quality of life.
MC will continue contributing to a carbon-neutral future by leveraging the expertise and networks it has developed in Japan and throughout Asia, collaborating with fellow BEC partner companies across a wide range of industries, including steel, aviation, and finance.
Demonstration Project of Compact LNG Filling Facilities for LNG Trucks in Hokkaido
MC and Air Water Inc. are jointly conducting a demonstration trials in Hokkaido using LNG-powered trucks (“LNG trucks”) and compact portable LNG filling facilities (“LNG filling boxes”).
The project addresses the challenges of electric vehicles (“EVs”) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (“FCVs”) for heavy-duty trucks, such as limitations in driving range and payload capacity, as well as their lengthy charging/refueling times. LNG trucks are the practical and immediate solution towards achieving a carbon-neutral society.
LNG trucks are capable of continuous long-distance travel exceeding 1,000 km, a range currently challenging for EVs and FCVs. Furthermore, LNG trucks are expected to reduce CO₂ emissions by approximately 10% or more compared to conventional diesel trucks.
These LNG trucks have driven a cumulative total of over 2 million kilometers since the commencement of the demonstration trials in April 2022. In November 2022, CO2 emissions were reduced even further by blending liquefied bio-methane (LBM) with LNG. LBM is produced from biogas derived from livestock manure in Hokkaido.
MC will continue to participate in these demonstration trials with the goal of introducing LNG trucks into society as a way of reducing CO2 emissions resulting from heavy-duty truck logistics.
Smari Business: Promoting Delivery Boxes by Effectively Utilizing Return Journeys from Existing Logistics Networks
Japan’s e-commerce market continues to grow due to social changes such as a declining birthrate, an aging population, the rise in double-income households, and the impact of COVID-19. At the same time, while parcel volume increases, labor shortages in the logistics sector are becoming a serious issue.
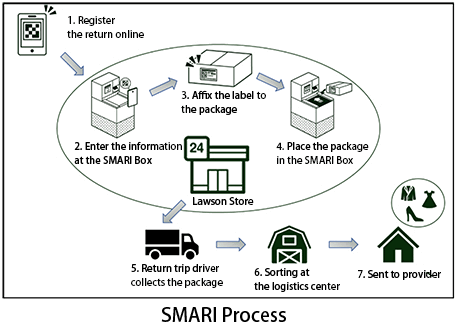
In partnership with Lawson, Inc., an affiliated company, MC launched the Smari service in April 2019. Smari uses Lawson's existing logistics network to enable non-face-to-face shipment of products sold on online flea-market platforms, as well as returns and rental items, that have increased with the expansion of e-commerce. As of 2025, the service has expanded to approximately 3,000 Lawson stores across the Tokyo, Kansai, Chubu, Hokkaido, and Kyushu regions, and has also been rolled out to additional locations such as train stations.
At roughly 14,500 Lawson stores across Japan—the primary locations for Smari—products are delivered seven to eight times each day from dedicated distribution centers. Smari is designed so that drivers, after completing their deliveries, pick up packages from the delivery boxes and transport them using the spare capacity in their trucks. This eco-friendly business model minimizes additional GHG emissions by utilizing return trips within the existing logistics network. Since it relies on existing routes, no additional personnel are required. Because shipments can be completed without face-to-face interaction, stores benefit from reduced checkout workload. Users also enjoy greater convenience: they do not need to fill out shipping labels or wait at the register, and can complete the shipment process in under a minute. At the same time, e-commerce companies and other shippers can expect improved customer satisfaction thanks to expanded return and shipping options.
Since 2023, MC has been collaborating with delivery box manufacturers to develop a new service that enables customers to send packages directly from their home delivery boxes. By making shipping and returns even more convenient and promoting the wider adoption of delivery boxes, this initiative aims to help address various social and environmental challenges, including those anticipated in Japan's logistics sector.
-

Smari Box -

Smari posting process
Attaining Real Estate Environmental Certification for Private Fund and Private REIT Management Businesses
Diamond Realty Management (DREAM)
DREAM, an MC subsidiary that forms and manages private real estate funds for Japanese and international investors, has established the following vision: “As a pioneer in real estate management, we will continue to be a company that is ahead of the curve in responding to the evolving needs of our stakeholders, and contribute to sustainable economic and social development and the preservation of the global environment.” Each employee upholds this vision and contributes environmental preservation and the resolution of social issues through business activities, aiming to help realize a sustainable society.
DREAM Private REIT Inc. (DPR), which focuses primarily on logistics centers, has achieved one of the top asset sizes in Japan. In the 2025 GRESB*1 Real Estate Assessment, DPR received a 5-Star rating for the fourth consecutive year, along with its eighth consecutive Green Star for outstanding performance. DPR was also selected as one of the Asia, Non-Listed Sector Leaders in the Diversified category for the second consecutive year.
DREAM has obtained multiple real estate environmental certifications for properties owned by the private funds and private REITs it manages. These include CASBEE Real Estate Assessment Certification*2, BELS Certification*3, Tokyo Metropolitan Small to Medium Scale Low Carbon Model Building*4 and ResReal/Flood Certification*5, and LEED*6 certifications.
By managing real estate with a strong commitment to sustainability, DREAM will continue contributing to maximization of societal well-being.
- *1GRESB
“GRESB” refers to both the annual benchmarking assessment and the management organization that evaluates the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data of real estate companies and funds. GRESB was established in 2009 by a group of major European pension funds who played leading roles in launching the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI). While GRESB originally stood for “Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark,” the term is now used more broadly as the scope of its assessments has expanded to include areas such as infrastructure. - *2CASBEE Real Estate Assessment Certification
The Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency (CASBEE) is a method for evaluating and rating a buildings’ environmental performance. The system comprehensively assesses various factors, including energy-efficiency, resource conservation, recycling performance, and considerations for the surrounding landscape. - *3BELS Assessment
The Building-Housing Energy-Efficiency Labeling System (BELS) is used to evaluate and label the energy performance of buildings. It applies to building for which this information must be provided to real estate business operators and other parties under the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings (Building Energy Efficiency Act), which came into force in April 2016. - *4Tokyo Metropolitan Small- to Medium-Sized Low-Carbon Model Building
Tokyo Metropolitan Small- and Medium-Sized Low-Carbon Model Buildings are those classified as A1 or higher under the Low-Carbon Building Benchmark, a standard for buildings with low CO2 emissions. This benchmark was published by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government in May 2012 to enable the evaluation of CO2 emissions in the real estate market. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government publicly lists the names of small- and medium-sized tenant buildings that are both a) classified as A1 or above and b) actively engaged in energy-conservation efforts as "Small- to Medium-Sized Low-Carbon Model Buildings." - *5ResReal Flood
ResReal is a certification offered by the Japan Real Estate Institute. It is Japan’s first certification program based on the quantification and visualization of a property’s resilience (strength, flexibility, recovery potential, and resistance) against natural disasters. Properties are certified based on factors such as robustness (location and building), redundancy, readiness, and substitutability. ResReal evaluates both “hard” resilience elements, such as a property’s location and building performance, and “soft” elements, including stockpiles of emergency supplies and disaster-preparedness training. The flood-damage version of ResReal provides a comprehensive quantitative assessment of a property’s resilience to flooding. - *6LEED
LEED (Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design) is a system for evaluating the environmental performance of built environments. It was developed and is operated by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), a U.S. nonprofit organization, and certification reviews are conducted by Green Business Certification Inc. (GBCI). LEED certification is issued at four levels—Platinum, Gold, Silver, and Certified—across six different certification systems.
Diamond Realty Management Green Building
Please refer to the ESG Data at the link below for information on Diamond Realty Management Inc.’s Green Building data.
Beyond Materials Corporation, a Specialized Strategy and Engineering Service Provider to Support Materials Suppliers
As societal and industrial needs evolve, particularly with the global shift toward decarbonization, requirements for new product designs in the electric vehicle (EV) and lithium-ion battery (LiB) sectors are becoming increasingly sophisticated and diverse. This trend is raising expectations for the functional materials used in these applications. MC and FEV Consulting GmbH, sharing a commitment to supporting the realization of a sustainable society, established the joint venture Beyond Materials to provide marketing and product‑development services to the materials industry. Beyond Materials functions as a bridge between material users in the automotive and other sectors and supports sustainable growth in the global materials industry. This initiative also advances Beyond Materials’ goal of contributing to sustainable development in global materials markets and supports MC’s mission to build net-zero, circular economies.



